Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring
Newcastle University
-
Unsupervised Learning
- Hart85 Method
- Combinatorial Optimization (CO)
- Fitting Hidden Markov Models (FHMM)
- Benchmark: Supervised Learning
Overview
Har85 Method
Combinatorial Optimization (CO)
Fitting Hidden Marcov Model (FHMM)
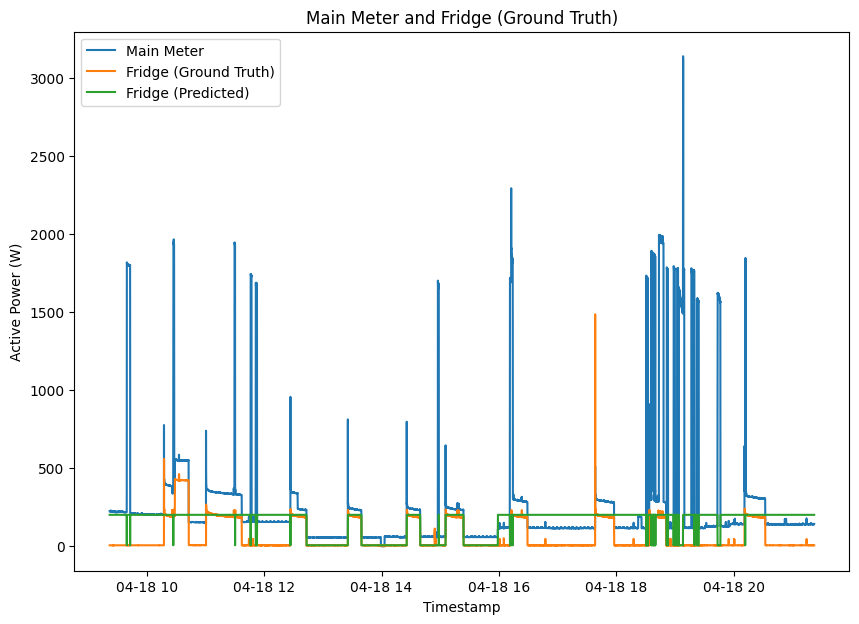
The Hart85 method was the pioneering work that initiated research in the field of NILM (Unsupervised Clustering).
Har85 Method (Feature + Clustering)
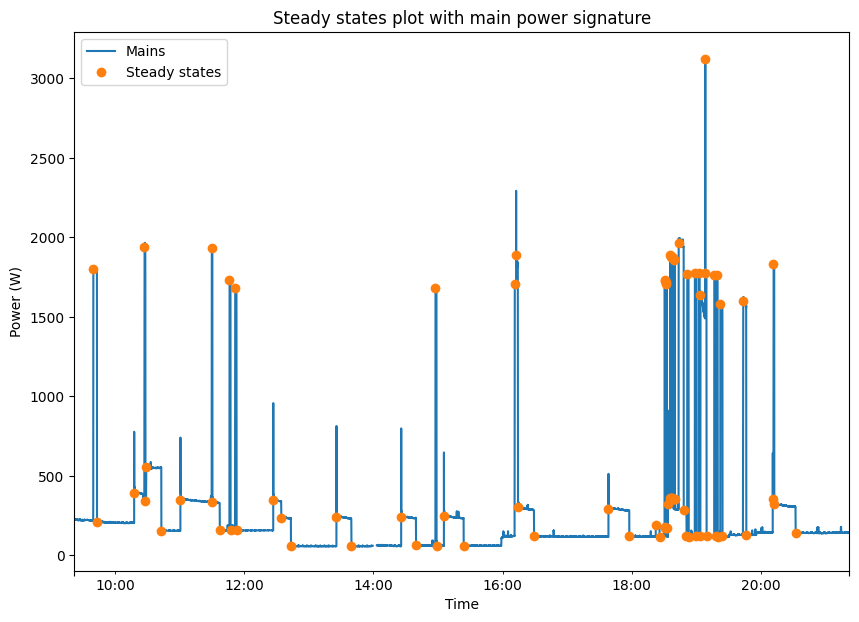
Step 1: Edge Detection (Find Steady States)
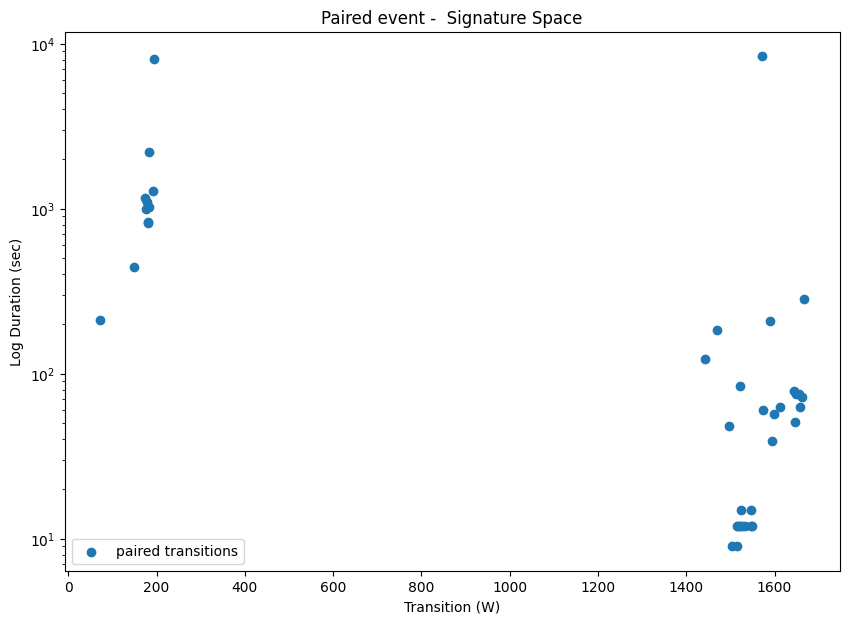
Step 2: Pair Events (Rising Edge & Falling Edge)
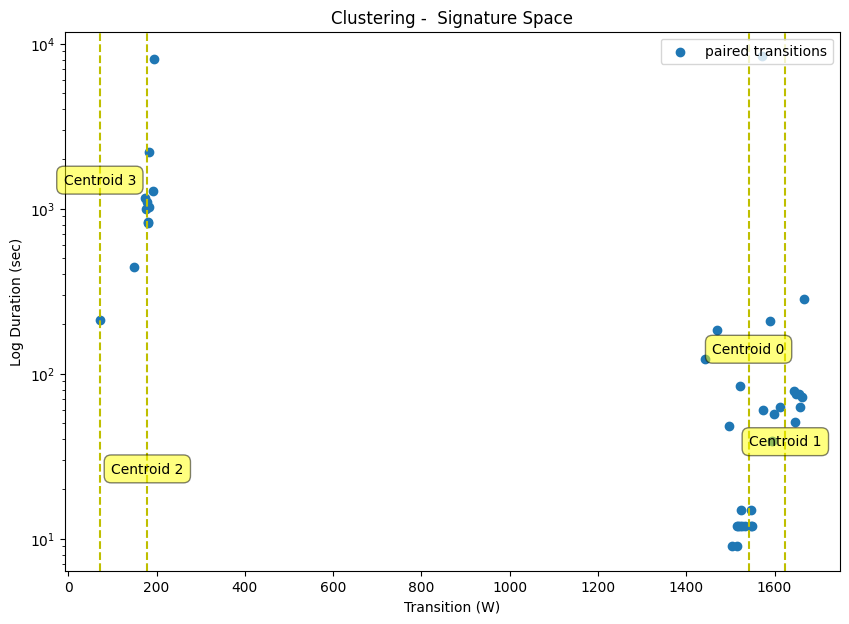
Step 3: Clustering (Transition & Duration)
Input: Transition (W) and Duration (second), require both rising edge and falling edge.
We can combine Agglomerative Clustering with Hart85 to achieve online learning (No TM).
Event Detection: Rehman, Attique Ur, et al. "Event-detection algorithms for low sampling nonintrusive load monitoring systems based on low complexity statistical features." IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 69.3 (2019): 751-759.
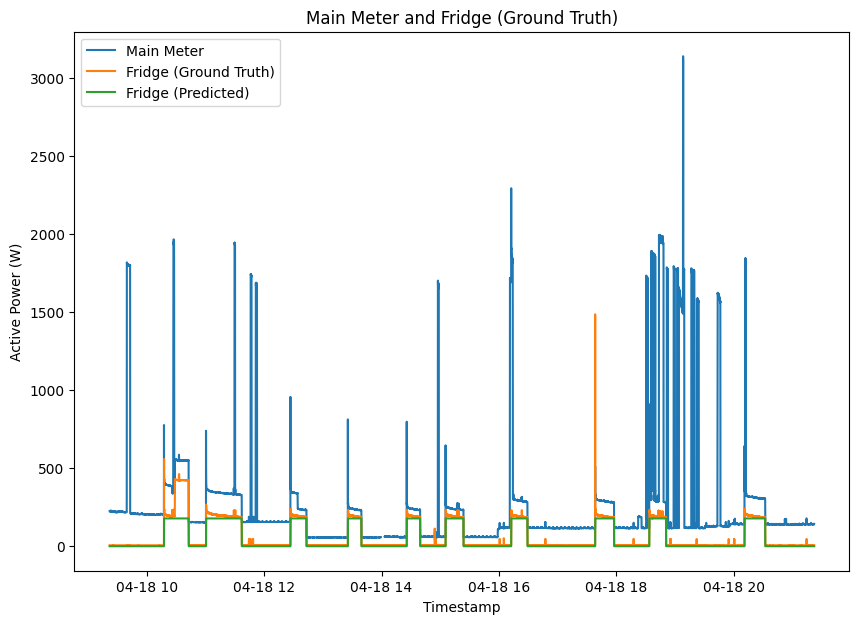
Combinatorial Optimization (CO)

The energy consumption of a fridge.
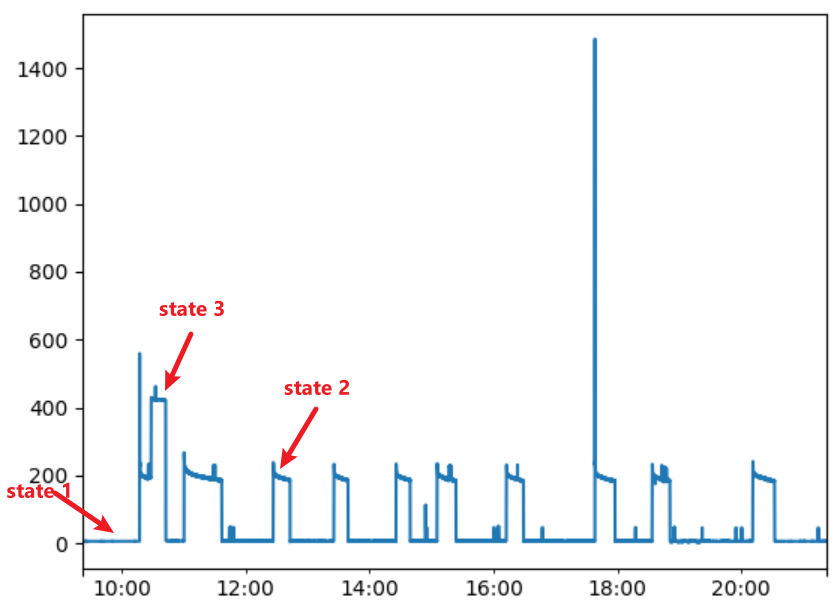
Use KMeans clustering to find states [ 0 (OFF), 193 (ON), 426 (ON)]
Input: Subsampled Readings
State Combination
App 1: [0, 193, 426]
App 2: [0, 13, 1618]
Find the combination of states that minimizes the total energy difference from the main meter.
The clustering requires the disaggregated readings of each appliance (Unavailable for online learning).
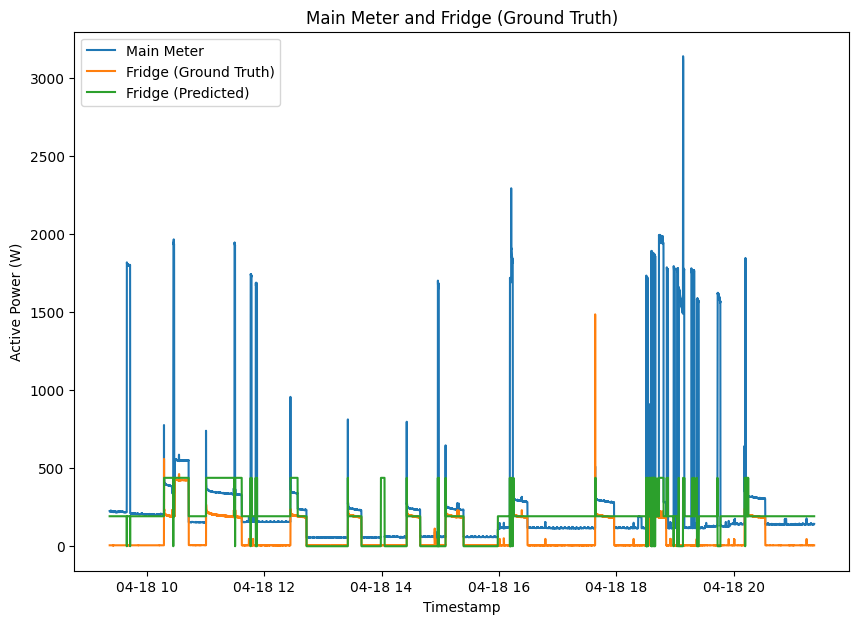
Fitting Hidden Marcov Model (FHMM)

The energy consumption of a fridge.

Use KMeans clustering to find states [ 0 (OFF), 193 (ON), 426 (ON)]
Input: A sequence of readings
Gaussian HMM
EM Algorithm / Combine FHMM
Viterbi Algorithm (Find most likely state sequence)
Decode HMM state sequence
Find the combination of states that minimizes the total energy difference from the main meter.
-
HMM requires the number of states to be known for each appliance.
-
The training process requires disaggregated readings for each appliance.
# Use Kmeans to find states for each appliance # Build HMM model for each appliance
states = cluster(meter_data, max_num_clusters) hmm.GaussianHMM(num_total_states, "full")
Benchmark (Supervised Learning)
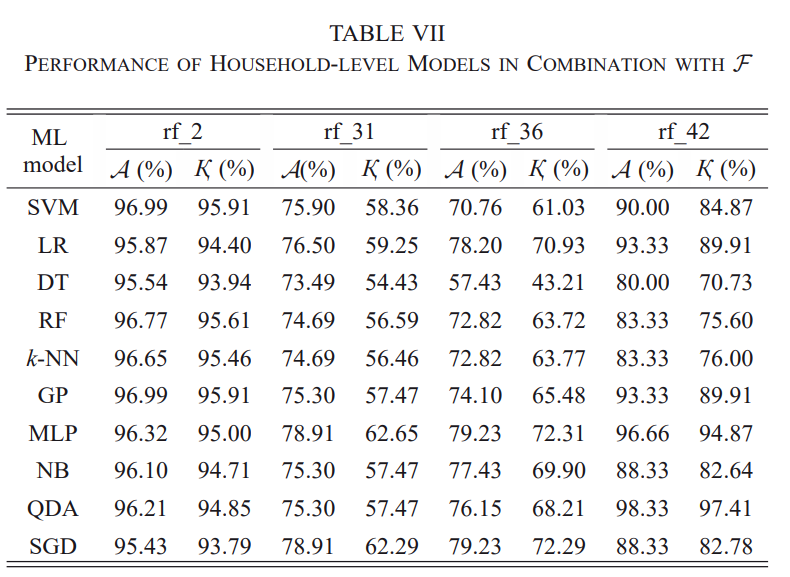
Virtually all existing supervised learning models yield promising results.
Can we pre-train on offline data and fine-tune online?
Thanks
